Brain-based learning, also known as neuroeducation, is an approach to education that draws insights from cognitive neuroscience to better understand how the brain learns and retains information.
By aligning teaching methods with the brain’s natural processes, educators aim to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of learning. Here are the key principles and implications of brain-based learning:
Engaging the Senses: The brain processes information more effectively when multiple senses are engaged. Incorporating visual aids, hands-on activities, also auditory elements in teaching can enhance comprehension and memory retention.
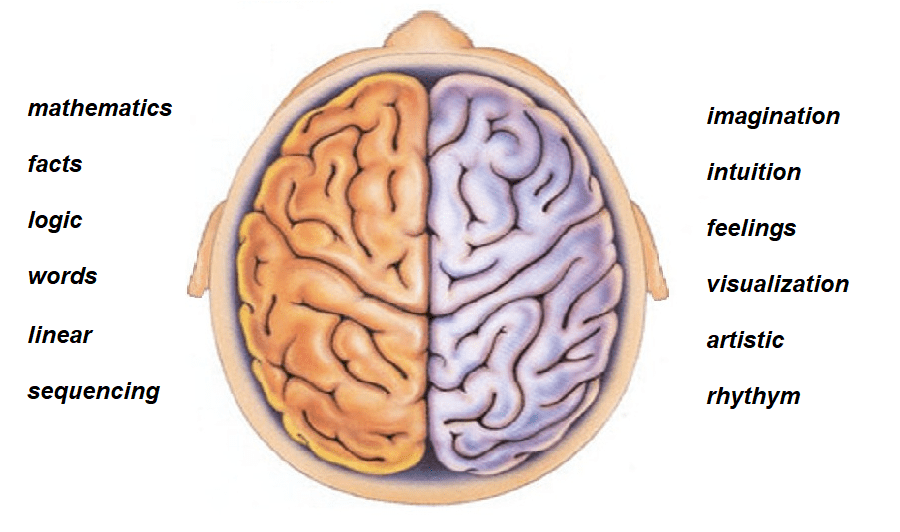
Active Learning: Active participation stimulates brain activity. Encouraging students to solve problems, ask questions, also engage in discussions promotes deeper understanding and memory consolidation.
Emotional Connection: Emotions play a significant role in learning. Positive emotions, such as curiosity and interest, enhance memory and cognitive processing. A safe and supportive classroom environment is essential for fostering emotional connections to the subject matter.
Respect for Individual Differences: Every brain is unique, and learners have different preferences and strengths. Brain-based learning recognizes the importance of accommodating diverse learning styles and abilities.
Stress Reduction: High stress levels can impede learning. Techniques like mindfulness and stress reduction exercises can help students manage anxiety also optimize their cognitive functions.
Chunking and Spacing: Breaking information into smaller, digestible chunks also spacing learning sessions over time can improve retention. This aligns with the brain’s limited capacity for processing information.
Feedback and Reflection: Frequent feedback and opportunities for self-reflection help learners monitor their understanding and adjust their strategies. This promotes metacognition, which is crucial for effective learning.
The Role of Sleep: Quality sleep is vital for memory consolidation. Brain-based learning acknowledges the importance of adequate rest for optimal cognitive function.
Brain Plasticity: The brain’s ability to rewire itself allows for continuous learning and adaptation. Educators can leverage this concept to encourage lifelong learning.
Interdisciplinary Learning: Encouraging connections between different subjects also disciplines can stimulate creative thinking and enhance memory retrieval.
Brain-based learning is not a one-size-fits-all approach but rather a set of guiding principles that can inform instructional strategies.
By incorporating these principles into teaching practices, educators can create a more brain-friendly learning environment that supports students in maximizing their cognitive potential, promoting deep understanding, and fostering a lifelong love of learning.
As our understanding of neuroscience advances, brain-based learning will continue to evolve and shape the future of education. 온라인카지노