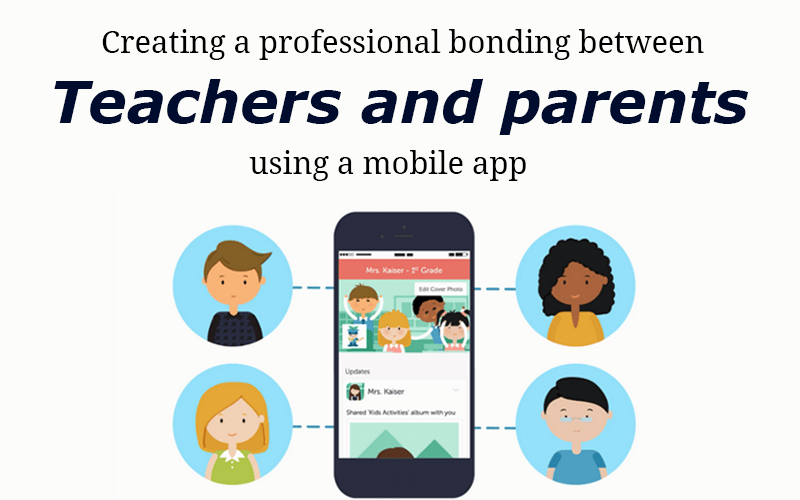
Online teacher-parent communication has become an integral part of modern education, bridging the gap between home and school.
It plays a crucial role in enhancing student success, fostering a collaborative educational environment, and promoting a deeper understanding of a child’s learning journey. Here are key aspects of online teacher-parent communication:
Regular Updates: Online communication allows teachers to provide parents with regular updates on their child’s academic progress, including grades, assignments, also test scores. This real-time feedback enables parents to address any concerns promptly.
Individualized Support: Teachers can share insights into each student’s strengths, weaknesses, also learning styles, helping parents provide more individualized support at home.
Behavioral Feedback: Online communication allows teachers to share information about a student’s behavior, participation, also social interactions, helping parents address any challenges.
Homework and Assignments: Teachers can use online platforms to share homework assignments, project deadlines, and classroom materials. This ensures that parents are aware of expectations for their child and can provide assistance or monitor progress accordingly.
Parent-Teacher Conferences: Online tools can facilitate scheduling and conducting parent-teacher conferences. This enhances the collaboration between educators and parents.
Two-Way Communication: Online platforms allow for two-way communication. Parents can reach out to teachers with questions or concerns. Fostering open communication also a strong partnership in their child’s education.
Support for Remote Learning: During situations like the COVID-19 pandemic, online communication became essential for supporting remote learning. Teachers can provide guidance also resources to parents to assist with at-home learning.
Emergency Notifications: Online platforms ensure parents receive timely updates about school closures, safety concerns, or other critical issues.
Transparency: Enhanced transparency in education can build trust between parents also teachers. Online communication tools can provide parents with clear insights into curriculum, grading policies, and school activities.
Parent Involvement: Engaging parents in their child’s education is a key to success. Online communication encourages parents to take an active role in their child’s learning journey.
Conclusion
Efficient online teacher-parent communication creates a collaborative ecosystem supporting academic and personal growth.
It enhances transparency, encourages active involvement, and ensures a child’s educational needs are met in both classroom and home. 온라인카지노사이트