Bloom’s Taxonomy is a hierarchical framework used in education to classify and categorize different levels of cognitive thinking and learning objectives.
Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues developed Bloom’s Taxonomy in 1956, and educators have widely adopted it to design effective teaching and assessment strategies. It consists of six distinct levels, each representing a different cognitive skill:
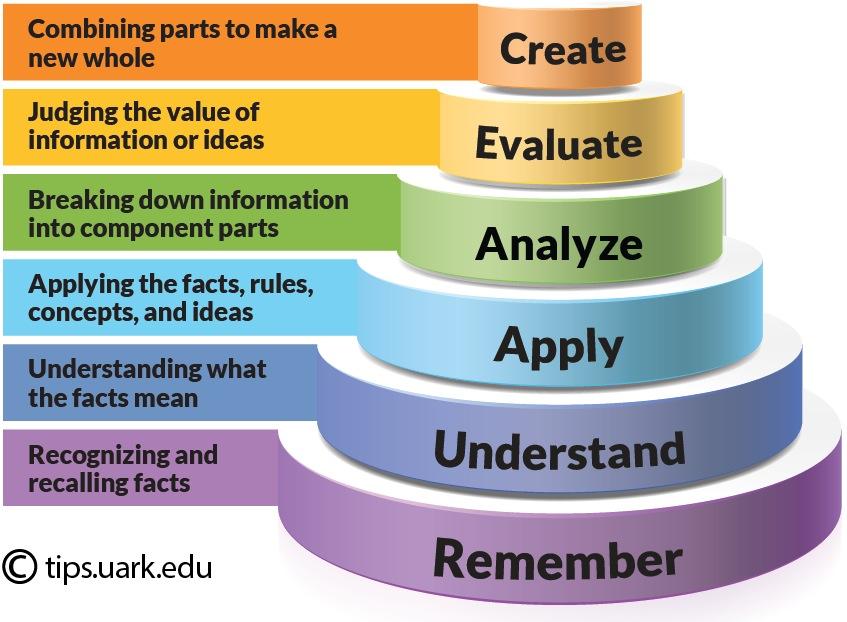
- Remembering: At the lowest level, students should recall facts, information, or concepts. This involves basic memorization also retrieval of knowledge. For example, teachers might ask students to list historical events or recite mathematical formulas.
- Understanding: This level requires students to comprehend and explain the meaning of the information they have remembered. They need to interpret and translate knowledge into their own words, demonstrating a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Applying: In this stage, learners use their understanding to solve problems or apply knowledge in new situations. They must take what they have learned and use it in practical contexts. For instance, they might use mathematical principles to solve real-world problems.
- Analyzing: At this level, students break down information into its component parts, identifying patterns, relationships, also underlying structures. They may compare and contrast different ideas or evaluate the validity of arguments.
- Evaluating: In the evaluation stage, students critically assess information or arguments, making judgments and decisions based on evidence and criteria. They may assess the quality, reliability, also relevance of information and arguments.
- Creating: The highest level of Bloom’s Taxonomy involves students generating original ideas, solutions, or products. They use their knowledge also skills to create something entirely new, demonstrating creativity and innovation.
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a valuable tool for educators as it helps them design instruction also assessments that align with specific learning objectives.
By identifying the desired level of cognitive skill, educators can tailor their teaching strategies to foster deep understanding and critical thinking.
Additionally, it provides a framework for creating well-rounded educational experiences that promote not only knowledge acquisition but also the development of higher-order thinking skills necessary for success in a complex and dynamic world. 온라인카지노사이트