Health disparities refer to differences in health outcomes between different groups of people. These disparities can be based on factors such as race, ethnicity, income, education, and geography.
One of the key factors that contribute to health disparities is access to healthcare. People who live in low-income communities or who lack health insurance are often unable to access necessary medical care, including preventative services such as vaccinations and cancer screenings.
Social determinants of health are the underlying social and economic factors that contribute to health disparities, including access to healthcare, education, employment, and housing.
This can result in higher rates of illness and disease among these populations.
In addition to access to healthcare, social determinants of health also include education and employment.
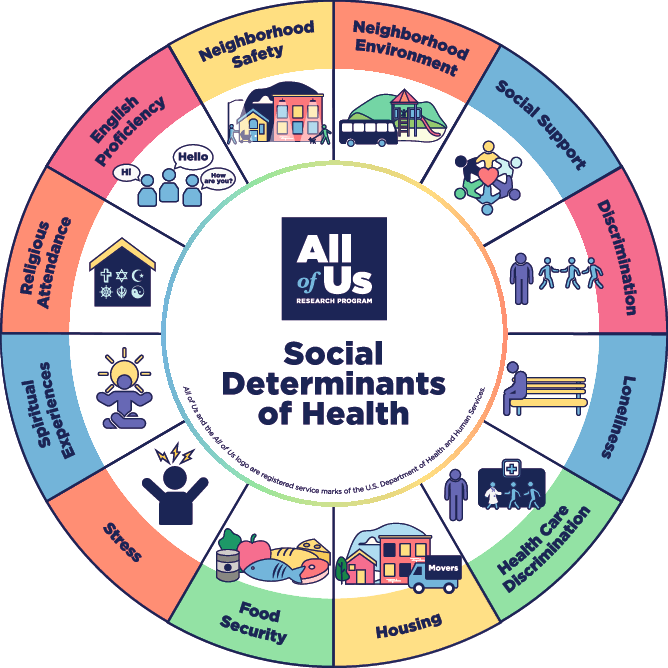
People who have higher levels of education and stable employment are more likely to have access to better healthcare and to live in neighborhoods with lower rates of crime and pollution.
They are also more likely to have access to healthy foods and to engage in regular physical activity.
Another important social determinant of health is housing. People who live in substandard or overcrowded housing are more likely to experience health problems such as respiratory infections, asthma, and lead poisoning. They may also be more vulnerable to environmental hazards such as mold and toxins.
Racial and ethnic disparities in health are another important aspect of health disparities. In the United States, African American and Latino populations have higher rates of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and obesity than white populations.
These disparities are linked to social determinants of health such as poverty, access to healthcare, and discrimination.
Discrimination and racism are also important factors that contribute to health disparities.
Discrimination can heighten stress, leading to health issues like high blood pressure, heart disease, and mental health problems.
They may also face limited healthcare access and barriers to other determinants like education and employment.
To address health disparities and social determinants of health, there are several strategies that can be employed. One approach is to increase access to healthcare and preventative services in underserved communities.
This involves expanding healthcare programs, funding community health centers, and incentivizing providers to serve underserved areas.
Another strategy is to address social determinants of health directly. This entails investing in education and the workforce, promoting affordable housing, and addressing environmental hazards like air pollution and lead exposure.
Reducing discrimination and racism is also important for addressing health disparities. This involves promoting diversity and inclusion, offering cultural competency training for healthcare providers, and tackling implicit bias in medical care.
Finally, community engagement and empowerment are key to addressing health disparities and social determinants of health.
This entails collaborating with community organizations to address underserved population needs, involving community members in decision-making, and advocating for policy change at various levels.
Conclusion
Health disparities and social determinants of health are complex, interconnected issues affecting individuals’ and communities’ well-being.
Addressing access to healthcare, education, employment, housing, and discrimination promotes health equity and reduces disparities.
This requires a multifaceted approach that involves collaboration between healthcare providers, community-based organizations, policymakers, and other stakeholders. 온라인카지노사이트
Be First to Comment