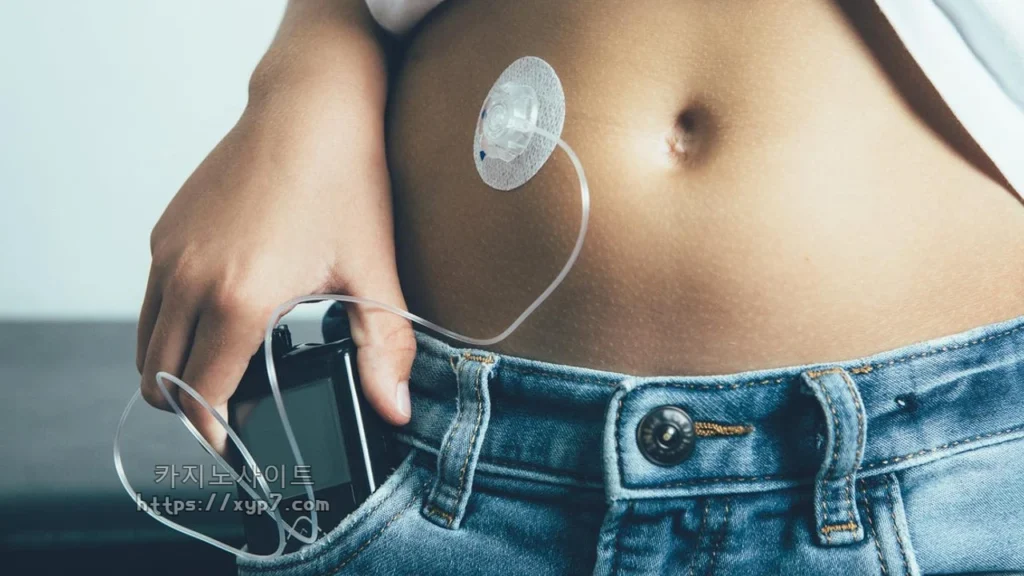
Diabetes: Understanding and Managing a Global Health Challenge
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects how our bodies process and utilize glucose, the primary source of energy for cells. It occurs when the pancreas either does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces.
This results in elevated blood glucose levels, leading to various health complications if left uncontrolled.

Types of Diabetes:
There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational. Type 1 is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks also destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Type 2 is more common and usually develops over time due to a combination of genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and obesity. Gestation occurs during pregnancy and can pose risks to both the mother and the baby.
Prevalence and Impact:
Diabetes is a significant global health challenge, affecting millions of people worldwide. Its prevalence has been steadily increasing, largely attributed to sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy diets, and rising obesity rates.
If not well managed, can lead to severe health consequences, including cardiovascular diseases, kidney failure, vision problems, and nerve damage.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Common symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurry vision, and slow-healing wounds.
Early detection and timely diagnosis are crucial for effective management and to prevent complications. Regular blood glucose testing and medical check-ups are essential, especially for individuals with risk factors.
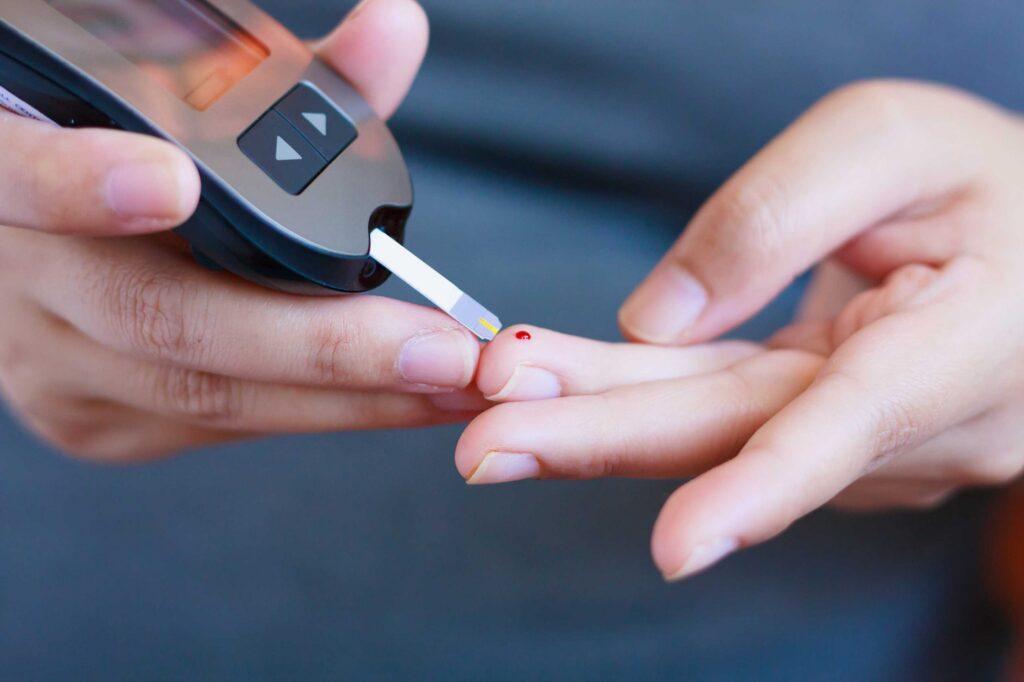
Management and Treatment:
The management of diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and, in some cases, insulin therapy. Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight, are central to diabetes management.
Medications like oral antidiabetic drugs or insulin injections help control blood glucose levels.
Diabetes Prevention:
Type 2 diabetes, in particular, can often be prevented or delayed through lifestyle changes. Eating a nutritious diet, being physically active, avoiding tobacco use, also managing stress are crucial components of prevention.
Public health initiatives and community awareness programs play a vital role in promoting healthy behaviors and reducing incidence.
Diabetes Research and Advancements:
Ongoing research aims to improve treatment options, enhance patient outcomes, and ultimately find a cure. Advancements in glucose monitoring technology, insulin delivery systems, and artificial pancreas development have significantly improved management.
The Role of Education and Support:
Education and support are vital for individuals living with diabetes. Proper self-management skills, understanding medication regimens, also monitoring blood glucose levels are essential for maintaining good health.
Support groups and diabetes educators can provide valuable assistance also empower individuals to take charge of their condition.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a multifaceted health condition that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention, diagnosis, and management.
With a focus on healthy lifestyles, early detection, and access to appropriate medical care, it is possible to improve the quality of life for those affected.
Raising awareness, advocating for research, and supporting individuals in their journey to manage the condition are crucial steps toward reducing the global burden of and improving overall public health. 온라인카지노사이트