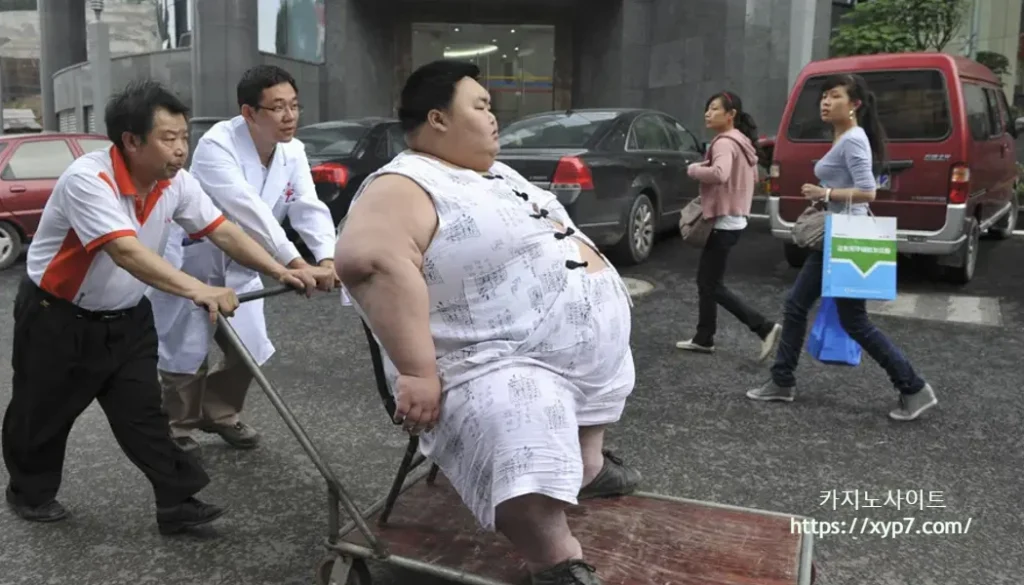
When Chinese health researchers first noticed the country’s growing waistline, they wanted to investigate further. In 1982, China’s Ministry of Health decided to conduct a large-scale study of the country’s diet to identify areas of malnutrition and understand the best areas to focus on food resources. But during their research, they found that the number of obese people in China was about 7 percent of the population (in contrast, in 1980, it was said that 26% of American adults were obese you are my). About ten years later, a study conducted in 1992 suggested that 15% of Chinese people are obese and about 30 million are obese in hospitals.
In other words, China’s population has doubled in ten years. Overweight and obesity are now an addition to China’s increasingly long health care plan. In 1990, the government launched the first campaign against smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and carefully considered the negative – always political – impact of pollution on the health of the country. As China becomes more prosperous, there has been a so-called “economic vulnerability” – an increasing awareness of depression as well as Alzheimer’s disease and other conditions related to longevity. Obesity has entered this group as decades of food shortages have returned to normal.
TV shows and radio shows discuss the negative effects of obesity on everything from marriage prospects to student test results to getting a job. “Fat camps” for children, fake diet pills, the widespread acceptance of liposuction, the explosion of gyms, and all kinds of quack diets are the subject of tabloid debate and speculation. Obesity in the image is not seen as a sensitive topic by media analysts and therefore the tabloid media has used to discuss obesity with a vengeance.
In the West, there has been a tendency to compare the “obesity disease” with the same evil found in food – the suspect if you want – trans fat, junk food and carbonated drinks. But, in China, it was the change in combination with the national cuisine that made the difference.
The truth is, especially for the urban population of China, food has changed a lot and seems to be constant in terms of volume and variety. Access to food has increased dramatically – supermarkets, hypermarkets, convenience stores. At the same time, the variety of foods has expanded, although many of the prepackaged foods are high in fat, salt, and sugar (HFSS). For example, the total value of processed foods and beverages with high HFSS food products has more than doubled that of fresh fruit and vegetable sales over the past 15 years. The diet has changed and the malnutrition of urban areas has now stopped, but not necessarily for the better.
Read: Your Appearance Affect the Way People Treat You
As new data has revealed China’s waistline is growing, the policy of targeting the poor and those who don’t eat enough food has also become a quest to understand why some people are putting their health at risk by eating limit. “From starvation to overeating in one generation,” a nutritionist from Guangzhou told me. Another person described it as an “economic advantage” in the new China and that, as more people own cars, the number of accidents has increased, the greater availability, accessibility and ability of food see some the Chinese are overdoing it and being overweight to the point of damaging their health. . In 2012, China’s Ministry of Health estimated that fewer than 300 million Chinese people were overweight out of 1.2 billion. This total makes China the second largest country after the United States in terms of population.
The increase in obesity rates is turning into a major health policy problem. A recent study on obesity and diabetes to date showed that the number of diabetes and diabetes is almost 10% and 16%, respectively, in across China, accounting for 92.4 million adults. have diabetes and 148.2 million adults have diabetes. Underdiagnosis is a major concern for health policy makers in China. It is believed that diabetes, both types 1 and 2, is underdiagnosed, since according to the Ministry of Health, only 30.2% of Chinese people have high blood pressure as a medical condition (and many people, that seems like a high estimate). As a result of research, China may have many diabetics, who do not know their condition or cannot get treatment. Their number can be increased from 1.5 to 2 million new patients per year.
Chinese health care providers are more aware of obesity and related health problems than they were just five years ago, said Ji Chengye of the Child and Adolescent Association of China Preventive Medicine. “China has entered. an era of obesity”. It is now the subject of many studies, media reviews and much awareness. For the most part, the government says unemployment and sedentary lifestyles are the main causes of the problem. Tian Ye, director of the scientific institute of the China Institute of Sports Science, said that the problem of weight gain and physical decline may be due to the lack of sports activities among young people, but funds have been received for participation programs. in many people.
Read: What You Must Know About Vitamin C Deficiency
In all areas – from exercise to nutrition – specific funding for obesity awareness programs remains low to non-existent. In China’s strict central planning system of limited budgets, awareness of problems can grow, but money and new methods are very slow to emerge, due to the five-year planning process. In 2009, as part of China’s $586bn (£384bn) fiscal stimulus package, the central government released billions for the health system, both in rural and urban areas.
However, none of these advances obesity prevention. Although the number of researchers in the field has increased, work at the ground level is still low. According to the China Institute of Nutrition and Food Hygiene in Beijing, the country has more than 10,000 nutritionists nationwide, but there is a need for at least four million , according to international standards. Caterer for 300 people.
China still has obesity laws. In 2007, when new obesity rates hit the headlines, some initiatives were put in place – the federal government mandated the construction of more playgrounds and passed laws requiring students to exercise or play sports. an hour a day at school. Although many playgrounds have been built, they are often poorly thought out and do not support more active sports, while many schools ignore the rules for physical activity (usually because of criticism from mothers and father of time lost outside of the university) or converting them by using time. Online Casino Games and Guide in Europe.
Similarly, the government’s policy to establish a workplace schedule was dismissed by employers as inappropriate when workers had clients to deal with. At the same time, the Chinese Nutrition Society launched a campaign – Eat Smart in Schools – which aims to develop healthy eating habits in schools. This focus on school meals follows research in Hong Kong, where it was found that lunch foods such as fried rice and noodles are high in fat, cholesterol and sodium. In 2006, Hong Kong launched a campaign called [email protected] to promote healthy eating nationwide. The campaign included the launch of a new school meal plan for primary school pupils to help caterers provide 300,000 pupils with appropriate meals in some 600 primary schools on a regular basis. China followed suit, although only schools in urban areas could afford the new lunch.
According to a 2012 study by the Children’s Hospital of Shanghai Fudan University, the number of Chinese children under the age of 14 with diabetes is increasing rapidly and has nearly tripled in the past 25 years. reported a significant increase in the onset of diabetes in young adults. MODY). MODY increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, which causes the exhaustion of insulin-producing cells associated with the aging process, in young and old people. In addition to the increase in type 2 diabetes in young people, it also means that many heart diseases, strokes and kidney failure – problems caused by diabetes – will develop in teenagers and young adults. Simply put, what used to be a chronic disease in mid-life in China is now a pediatric problem in children under the age of ten. All of these factors will have a significant impact on China’s healthcare budget in the future. Dried apricots on the market in Uzbekistan. Event Sponsorship
Estimates of change – compared to US and UK prices for an obese patient in China, and prices shown to reflect lower treatment costs – the annual cost increase for China has set the obesity and overweight population at 155 billion dollars. In the next decade, China’s health planner will dig deep to tackle obesity.